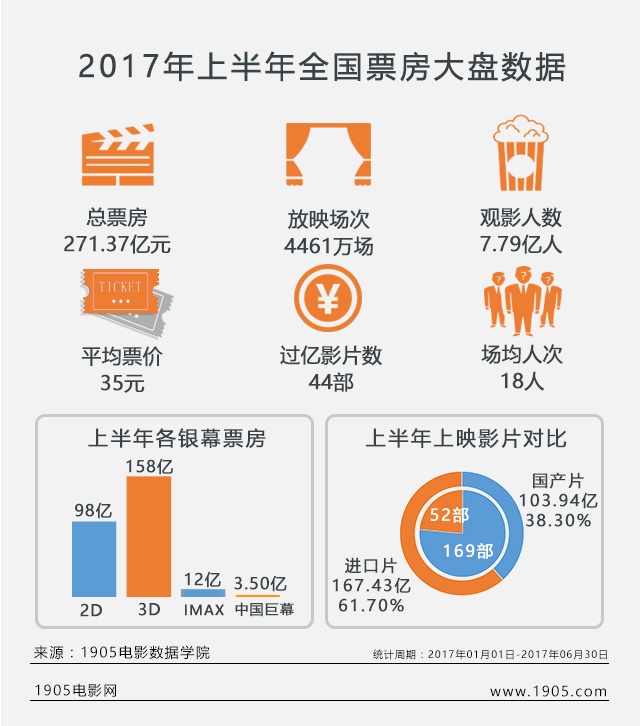
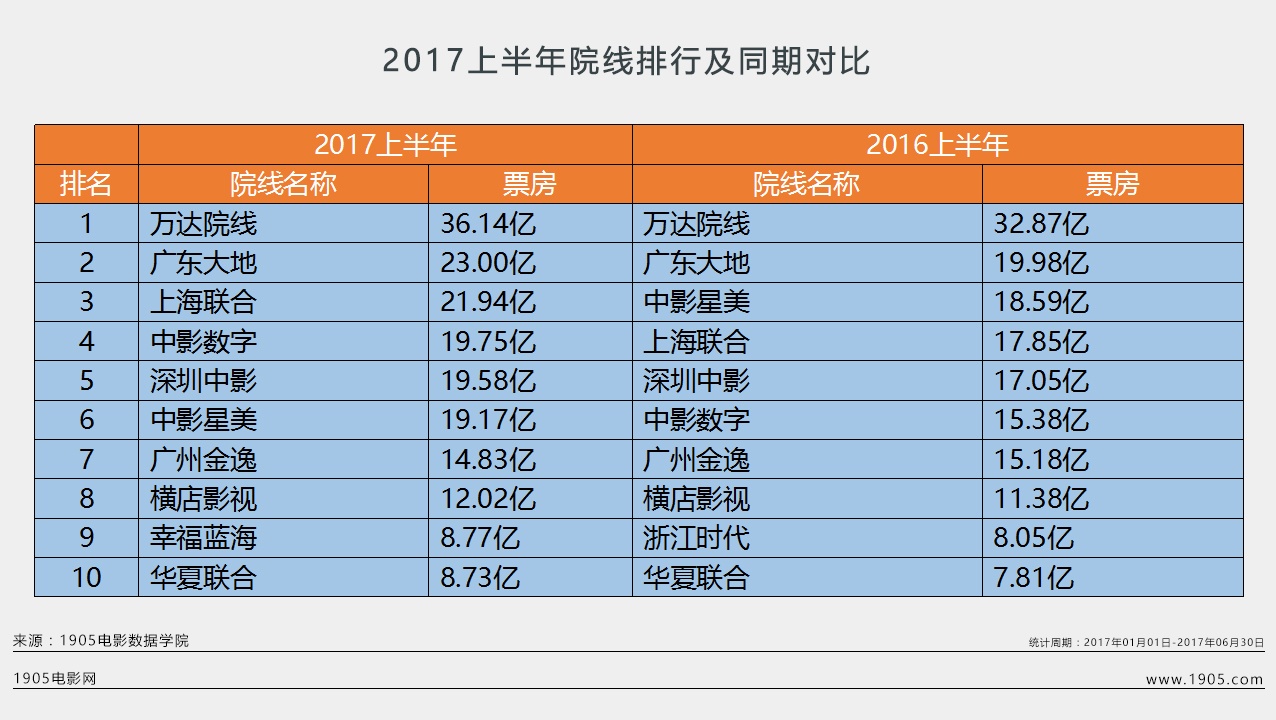
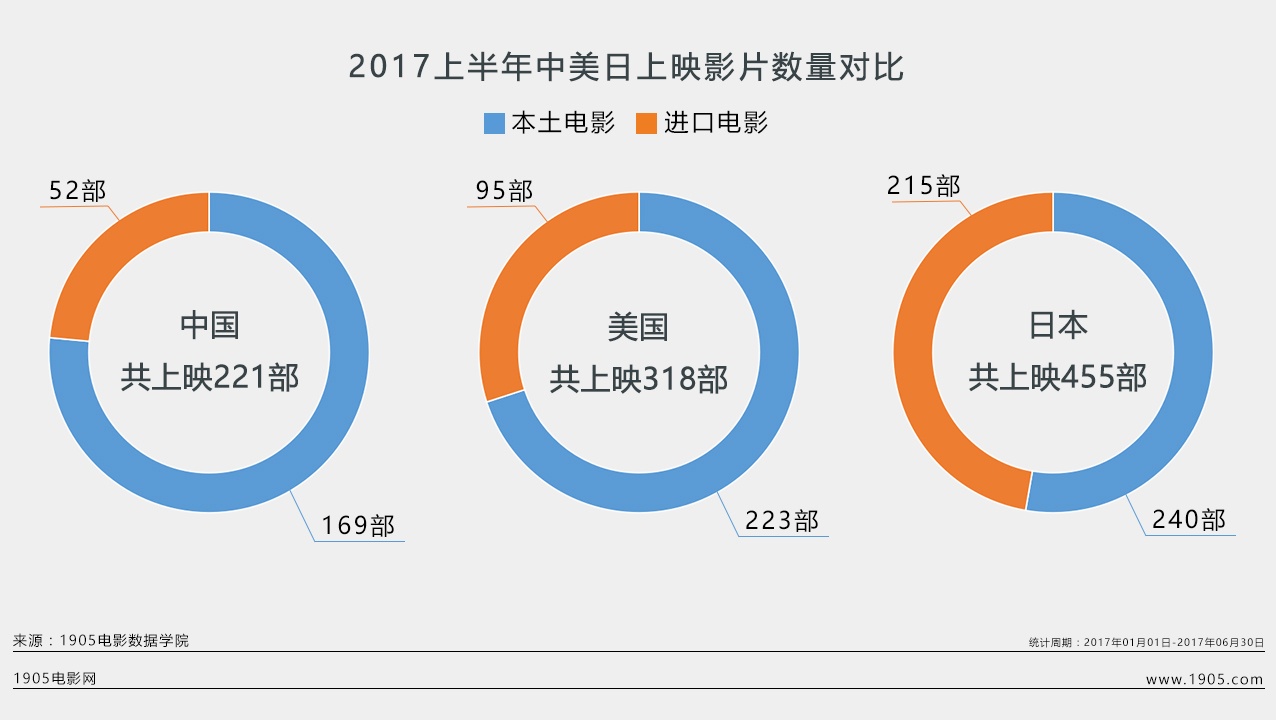
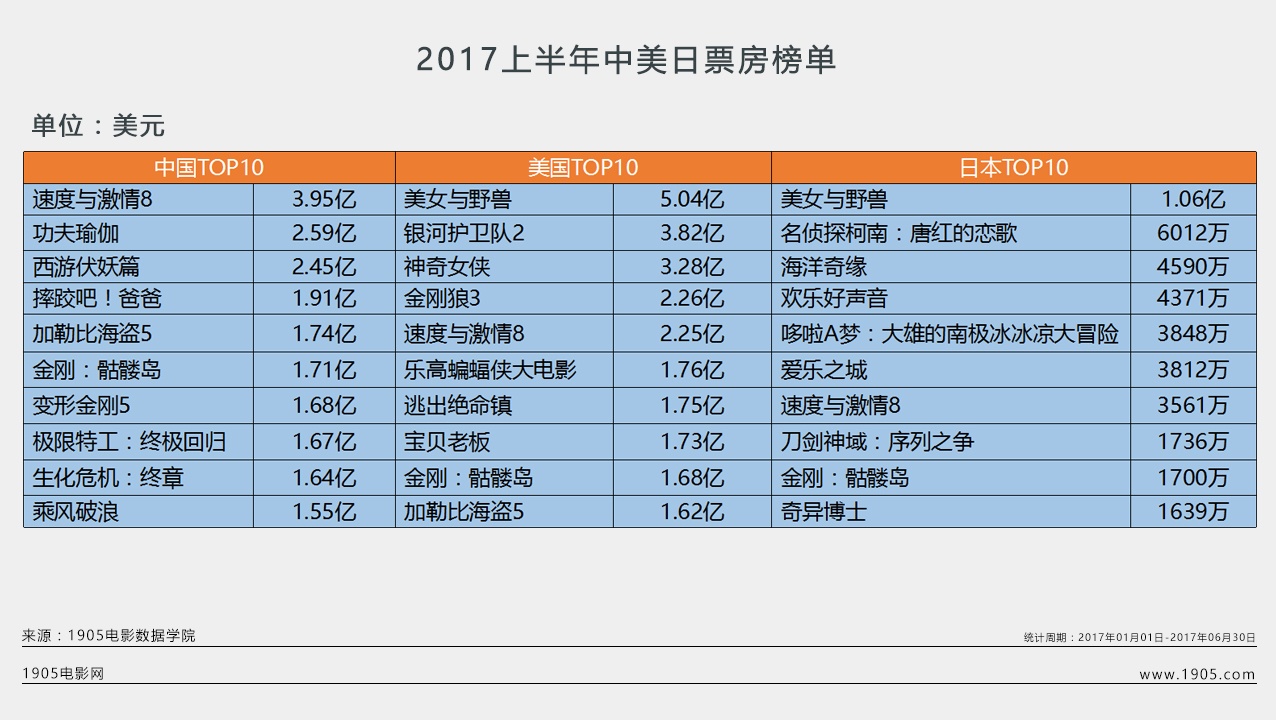
Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China released the research report "Ten Questions about American Democracy" on December 6. From which ten aspects did the report reveal the true face of American democracy with facts? Why is it that it is not the people who can be the masters in the United States, but "one country with six masters, there is no democracy"? Why do you say that American democracy has become a tool for a few people to seek personal gain, and it has become a cover and excuse for the United States to maintain hegemony, interfere in other countries’ internal affairs and undermine international order? How do Americans question their democracy? How has the hegemonic behavior of the United States holding high the guise of democracy been criticized by the international community? "Global Sight" invited the publisher of the research report to make an in-depth interpretation.
What is the background of this report?
The full text of the research report "Ten Questions about American Democracy" is 23,000 words, which puts forward ten sharp questions about American democracy. Under what background did this report come into being?
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China: I think the biggest background is that the United States is "sick" and China scholars have to "diagnose" him. At present, the biggest focus of American democracy is that he is a "sick man". He also wants to hold a "democracy summit" to distort the whole international public opinion, distorting the international public opinion that he is the boss and the representative of democracy, and to fight against the so-called "non-democratic countries" and then "protect" democracy. This is a completely morbid self-aesthetic, and we scholars in China should point out this morbid state and correct it for him. On this premise, I think the report Ten Questions about American Democracy has played a very good role as a whole, and diplomats at the conference site, including foreign media reports today, have given very positive comments.
Question: Democracy of the majority or democracy of the minority?
There are ten questions in this report. The first one sharply raised the question "Is American democracy the democracy of the majority or the democracy of the minority?" The report also used a lot of facts to show that the United States is in the name of "democracy". It is Money-cracy, Gun-cracy, White-cracy, Media-cracy, military-cracy and Drug-cracy that can embody their will. Judging from the "six masters", is American democracy the democracy of the majority or the democracy of the minority?
Diao Daming, an expert on American issues: American democracy is obviously the democracy of a few people, and it is a democratic chaos in which a few people override the majority. These "six masters" are actually special elite interests. In fact, under the framework of this system in the United States, the presidential election is ultimately a key vote, a key person, or a minority. For example, at present, congressional elections, redistricting and so on are still operated by the political elites of the two parties, which finally leads to a state that voters are not free to choose but have no choice. So who are these minorities or so-called elites? In fact, the most important thing is actually capital, and all power is for the service of capital. For example, we recently saw that the bickering between the two parties was driven by special interests, which was driven by a minority of 1%. As a result, 99% of the public did not get any response under this democratic framework, which eventually led to the situation of "one country, six owners, but no democracy".
Second question: does it achieve power checks and balances or lead to power abuse?
The founders of the United States designed the "system of separation of powers and checks and balances" to prevent power corruption and abuse. However, in this process, we will find that the United States has gone further and further. For example, the American media will say that the separation of powers system in the United States has collapsed, the morality of the highest power department has gradually declined, and the American people’s trust in the US government has disappeared. In this way, can American democracy achieve its original intention and achieve the separation and checks and balances of power?
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China: I think it seems that it can’t be realized completely at present. There is a word called "polarization" in the United States, and it is also called "absolute polarization". This kind of fierce struggle between the two parties used to be debated, and we can still be friends in the future. At present, more than 80% of the staff of the two parties think that the other party is extremely annoying, so at this time, there is a phenomenon of "polarization" and mutual veto. What’s more important, because this "polarization" phenomenon uses various means to abuse legislative power, executive power and judicial power, more than 80% of the American people believe that this system in the United States needs reform or thorough reform, so the American people’s trust in the American government has almost reached freezing point.
Three questions: improve people’s well-being or deepen people’s suffering?
According to the data of USDA, in 2020, 10.5% families and 38.3 million people in the United States will face hunger, and 14.8% families with children and 6.1 million children will face hunger. In addition, according to statistics, in 2020, at least 580,000 Americans will be homeless, and more than 220,000 people will sleep on the streets. So, does American democracy improve people’s well-being or deepen people’s suffering?
Diao Daming, an expert on American issues: It should be said that for most people, it is definitely a deeper disaster. We just talked about that American democracy itself is a state in which the minority is above the majority, but for the majority of the general public, they may be called out in the election to play a role, so they are called voters. But for these so-called voters with votes, the result of political manipulation by the two parties is that voters come out to be manipulated, fooled and mobilized during the election, and then no matter who is elected after the election, these voters will be sent back to the "cold winter" and continue to "hibernate". The "cold winter" is of course very harsh, so in fact, during the whole campaign, they will continue to "paint cakes" and say that they will serve the middle class, but in the end, no one will take care of these voters. In particular, there are some homeless people, such as those who are still hungry and cold, who don’t go back to the election at all, which means that they are not votes. For politicians, they are not even votes and they are not citizens at all, so politicians will not respond to their demands at all. Therefore, this kind of democracy, which has no response to the people, is definitely a kind of fake democracy.
Four questions: Defend freedom or hinder freedom?
All along, the United States loves to flaunt American democracy and defend freedom, and also calls itself "a model of freedom and a beacon of hope." Speaking of freedom, during the global epidemic, "mask freedom" actually occurred in the United States, that is, flaunting whether I wear a mask is my freedom and has nothing to do with epidemic prevention. What does this "overloaded personal freedom" have to do with the so-called freedom in the United States?
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China: In fact, the words "overloaded freedom" and "overloaded democracy" originated from Samuel Huntington, a very famous late American political scientist. Professor Huntington predicted at that time that if the United States continues to do so, all your power and freedom you admire have been overloaded, exceeding the limits you should bear. Therefore, American democracy is now in the name of freedom, and the ultimate goal is to hinder freedom. It means that true freedom and all freedoms should be relative, freedom under the framework of law and system. If you can do everything, such freedom is ultimately limited to your personal freedom and destroys the freedom of others. For example, if you say that I love wearing a mask, you will hinder the freedom of others at this time. Therefore, many politicians in the United States use the media and public opinion to publicize the so-called absolute freedom and use populism to win votes. In the end, it seems that it protects the interests of some people and advocates the freedom of some people, but actually destroys the freedom of all people.
Question 5: Protecting human rights or violating human rights?
The United States regards "protecting human rights" as one of the reasons for promoting American democracy abroad. However, the data in the report is shocking. For example, in 2020, the number of murders in the United States surged by 25% year-on-year, and the United States is also the country with the highest gun-related crime rate among developed countries. In addition, by the beginning of December 2021, about 50 million people in the United States had been infected with COVID-19, and the death toll was about 800,000. The number of infected people and deaths ranks far first in the world. How do you think that while the United States advocates democracy under the banner of human rights, it is difficult to guarantee even the most basic right to life of the American people?
Diao Daming, an expert on American issues: This is actually very ridiculous and ironic. The so-called democracy in the United States can’t even guarantee the people’s most basic human right, the right to life. How can such a so-called American democracy continue to be sold to the world? In fact, the American people have no rights at gunpoint, and the proliferation of guns in the United States is actually a chronic disease. On the issue of gun rights, both parties in the United States are driven by some special interests. As a result, when they drive relevant legislation or political struggles, they have no regard for the basic human rights of ordinary people who die in vain at gunpoint every year. So all this means that there is no right at gunpoint, and there is no right in the ward. That is to say, since the epidemic, the two parties in the United States are still politicizing epidemic prevention without considering the safety of the people in the absence of such a fragmented governance as federalism. It is not the attitude of putting life first and people first, or considering the number of votes, etc. There is no human rights consciousness and driving intention at all, and it is completely for the service of a few elites. The public is not regarded as life, but as votes, so it should be a great failure of democracy.
Six questions: promote unity or lead to division?
The United States is a federation of 50 states, and democracy should promote the unity among the states. The United States is still a multi-racial country, and democracy should also promote racial unity. However, the United States has not done well in these two aspects. Does the so-called American democracy promote unity or lead to division?
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Institute of Finance, Renmin University of China: The full name of the United States is translated into Chinese and called the United States of America. Now, many scholars have said that this full name should be changed and should be called the United States secession. Now more and more scholars come out to say that the United States may split up. Now almost 50% of Trump supporters and 50% of Biden supporters in the United States say, let’s divide our country. It may be better to divide it. Then, because of this division, there is now a new word that the United States has a cold war. The difference between this cold war and the past cold war is that this is an internal cold war or a cold civil war. There was a civil war in the United States, which was not solved by guns and cannons, but by a cold war and division. This situation is brought about by his democracy. Through election campaigns, they emphasize that they are different from others, which leads to more and more division and differentiation. Therefore, we see that every election in the United States is like two countries. Therefore, Americans themselves are very worried, saying that the period of "the country will not be a country" is getting closer and closer.
Seven questions: Realizing dreams or bringing nightmares?
The survey shows that Americans’ national self-confidence has been seriously frustrated. In 2014, 28% of Americans believed that the United States was the greatest country. By 2019, the proportion of people who think that the United States is the greatest country in the world will drop to 24%, while the proportion of people who think that other countries are greater than the United States will rise to 21%. From the historical perspective of 2021, what does American democracy actually bring to people, more dreams or nightmares?
Diao Daming, an expert on American issues: What the United States has brought to the people is obviously a nightmare, and it should even be said that the state of American dream is broken. To a large extent, it is because the entire political system, including the absence of democracy and the complete failure of social governance, has caused any American public to live in the United States. There is no so-called happiness, which is a very important factor. In fact, some scholars in the United States are also discussing that the most important thing in the so-called American dream is the mobility of classes. Up to now, the solidification of this class in the United States is very serious. At the same time, the dilemma of class mobility has also led to the middle and lower classes, especially some ethnic minorities, being completely locked in the bottom space. Therefore, it leads to the complete solidification of the class and the emergence of the privileged class, which is an important embodiment of the American dream. In addition, the American dream is closely related to "polarization". Republicans and Democrats, conservatives and liberals have completely different interpretations of the American dream, and one side’s American dream is also a nightmare for the other. Therefore, when there is no way to form a unified state in the future development direction of the country, it means that it is difficult for the country to form some consensus to promote some reforms that are conducive to national development. In addition, many data show that American young people have a very high degree of dislike and distrust of the American dream, which means that this country has no future.
Eight questions: improving national governance or leading to system failure?
As the world’s largest economic power, the level of disaster response in the United States has dropped significantly in recent years. It is especially manifested in "ineffective risk prevention", "slow rescue and disaster relief" and "officials sitting on the sidelines", which not only hurt the American people’s trust and pride in the country, but also make the international community wonder "Is American democracy improving national governance or leading to system failure?"
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China: The American economy has been in a downturn for years. The wealth of the American people has not increased for 20 years, and the young people in the United States have no hope. Where are these reasons? The reason is that this country has become incompetent. In the past 20 years, we have seen many disasters in the United States, such as hurricanes and some emergencies. As a result, we suddenly found that this country and this government could not mobilize resources. When the epidemic came in China, a hospital was built in 10 days, and a building collapsed in Florida, USA. For six days, the whole rescue team did not move, so such a country’s system has been disabled and it has no ability to manage the country. We will see many phenomena that make us stunned. For example, the instructions of the federal government can’t reach the local level. For example, a high-speed rail in California has not been started for 20 years. Under this democratic system, the people have completely lost hope for this country. For the future, more and more people think that the American dream cannot be realized, and they are already writing obituaries for the American dream.
Question 9: Will it bring development and prosperity or disaster and turmoil to other countries?
The United States exported American democracy to other countries in the world in an attempt to transform other countries into democratic countries, but the result was to disrupt other countries. Does American democracy bring prosperity or disaster to other countries?
Diao Daming, an expert on American issues: In fact, in the diplomatic history of the United States, the United States "painted cakes" for other countries on the grounds of democracy, and this way of imposing democracy on other countries should be said to be "addictive". We know that any country should choose its own development path according to its own historical path and the reality of its own national conditions, including those that are more in line with public opinion. Including the forms of democracy, should also be varied, and there is no best but better. However, the United States imposes democracy on others in various ways and monopolizes the right to interpret democracy, which also interrupts the development path of free choice of other countries. This in itself is actually undemocratic and hegemonic on the grounds of democracy. Under such circumstances, it is impossible to bring too good development to other countries. More importantly, because of his hegemonic practice, under the guise of democracy, he essentially controls other countries to train agents to plunder resources, so as to constantly grab so-called geopolitical or energy interests, resulting in his own benefits, completely ignoring the long-term development sustainability of relevant countries or regions. Some places that accept democracy peddled by the United States are the worst developed places now. Therefore, on these issues, the United States should give the world an explanation and pay for these failures.
Question 10: Maintaining world peace and development or undermining international order?
We don’t respect the national conditions of other countries, and force other countries to adopt the American democratic model through military intervention and economic sanctions of dollar hegemony. We can’t help but ask, when the American democratic model has aroused widespread doubts from its own people and other countries in the world, is it to maintain world peace and development or undermine the international order?
Wang Wen, Executive Dean of Chongyang Financial Research Institute of Renmin University of China: The United States has obviously destroyed the international order and brought turmoil and disaster to the world. The key is that the United States controls the right to speak in the world. We have observed that in the past 100 years, the United States has launched wars, provoked wars and intervened in foreign countries the most. We said in the report that from 1880 to now, the United States has carried out more than 390 military interventions abroad, but his words are very powerful. Look at his invasion of Iraq. This war is called the Iraq War. When he invaded Korea, his name was the Korean War, and he invaded Vietnam. He named his past history after other countries, giving people the impression that these wars had nothing to do with the United States. Therefore, it seems that the United States is not so militaristic in our minds and is biased by his right to speak. Therefore, when we come back, we will see that in fact, in the report, a lot of words were quoted from the United States to evaluate itself as "refugee manufacturing machine". Since September 11, 37 million refugees around the world thought that the war launched by the United States after September 11 was born. The United States is not only a police country, but also a military country and a war country. The whole state machine was set up for war, so such a country certainly brought turmoil and disorder to the world.
Democracy is the common value of all mankind. The United States has no right to monopolize democratic standards, impose its own political system on others, and even have no right to form gangs, fight against differences and provoke division and confrontation under the guise of "democracy". The United States should implement its stance of not engaging in a "new cold war" and do more things that are conducive to the international community’s joint response to global urgent challenges such as the COVID-19 epidemic, the slowdown in economic growth and the crisis of climate change, instead of running counter to the spirit of helping each other in the same boat.